

In this tutorial, we will explore how to build a conversational agent with Redis using Flowise. Flowise is a powerful, open-source, and user-friendly AI platform that allows you to build and deploy conversational agents (and many other LLM flows) quickly using a simple and intuitive interface.
Normal LLMs (Large Language Models) like GPT-4 are general-purpose models trained on diverse datasets to perform a wide range of language-related tasks, such as text generation, translation, summarization, and more.
Conversational agents, however are more sophisticated and designed specifically for managing conversations effectively. They often integrate multiple specialized agents or modules to handle specific tasks, providing a comprehensive and interactive experience.
User question:
`Who won the latest 2024 elections in India?`
Normal LLM (GPT-4) response:
`Sorry, I don't have real-time access to current events or updates, including recent election outcomes. To find out who won the latest 2024 elections in India, I recommend checking the most recent news on a reliable news website or a trusted media outlet.`
Conversational agent response:
`Prime Minister Narendra Modi's Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) and its National Democratic Alliance (NDA) won the most seats in the latest 2024 elections in India.`
- A normal LLM cannot answer questions about the latest news, projects, etc., as it is not trained on real-time data.
- In contrast, a conversational agent can handle such queries because it integrates an LLM at its core along with other specialized agents to manage specific tasks. In our conversational agent example, we will use ChatOpenAI combined with a SearchAPI agent to answer questions about the latest news, weather, and other real-time information.
- The SearchAPI agent is a specialized module capable of fetching data from Google search results, enabling our conversational agent to provide up-to-date and relevant answers.
- We can use multiple specialized agents like SearchAPI, Calculator, Python Interpreter, Custom Tool, Custom Function/ API, etc., to enhance the capabilities of our conversational agent. LLM will pick the right tool to handle specific types of queries.
There are different ways to install Flowise. For this tutorial, we'll use the docker compose method to install Flowise.
Step-by-step instructions
1> Clone the Flowise repository from GitHub
git clone https://github.com/FlowiseAI/Flowise.git2> Navigate to the docker folder
cd Flowise/docker3> Copy the .env file: Copy the example environment file and rename it to .env. This file contains configuration settings for your docker containers.
cp .env.example .env4> Start the docker application: Use the following command to start the docker application in detached mode. This command will download the necessary docker images and start the Flowise application.
docker-compose up -d5> Access Flowise in your browser: Open your browser and navigate to http://localhost:3000 to access the Flowise application.
6> Stop the docker containers: If you need to stop the docker containers, you can do so with the following command:
docker-compose stopBy following these steps, you will have Flowise up and running on your local machine, ready for you to start building and testing your conversational agents.
Step-by-step instructions
1> Navigate to the Chatflows menu: Open your browser and go to http://localhost:3000. In the Flowise application, navigate to the Chatflows menu.
2> Create a new chatflow: Click on the `+ Add new` button to create a new chatflow.
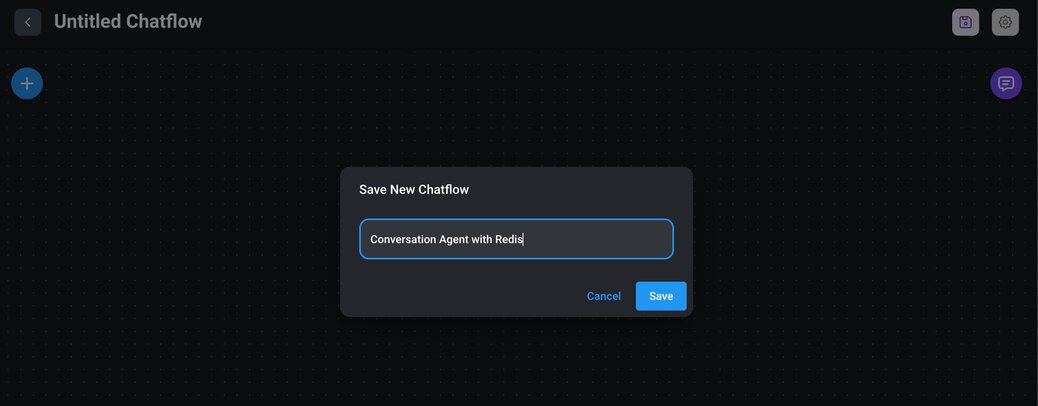
3> Save and name your chatflow: Click on the save icon. A prompt will appear asking you to name your chatflow. Enter a meaningful name that describes the purpose of your chatflow.
By following these steps, you will create a empty chatflow in Flowise, setting the foundation for building your conversational agent
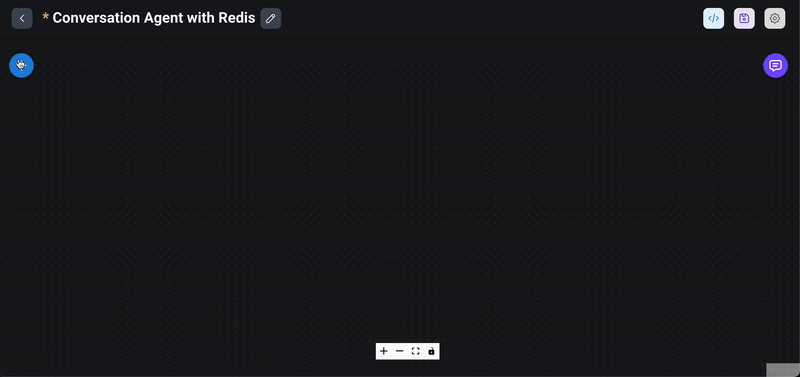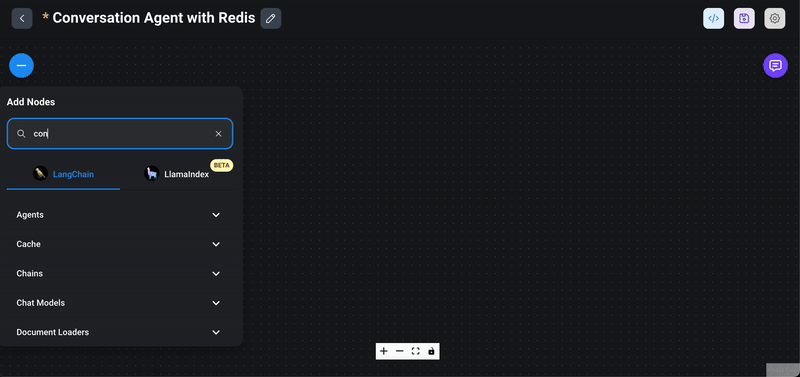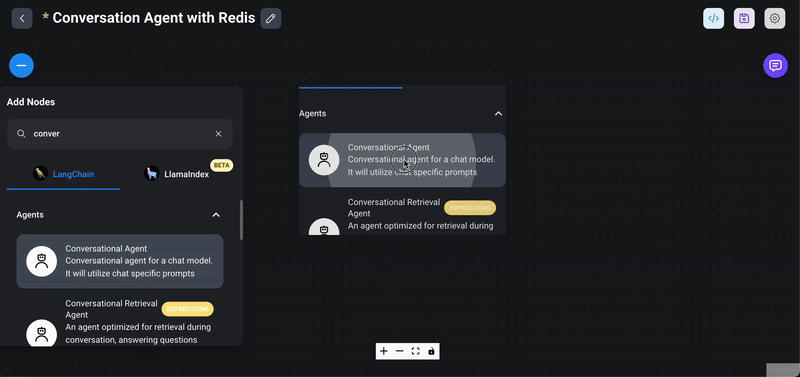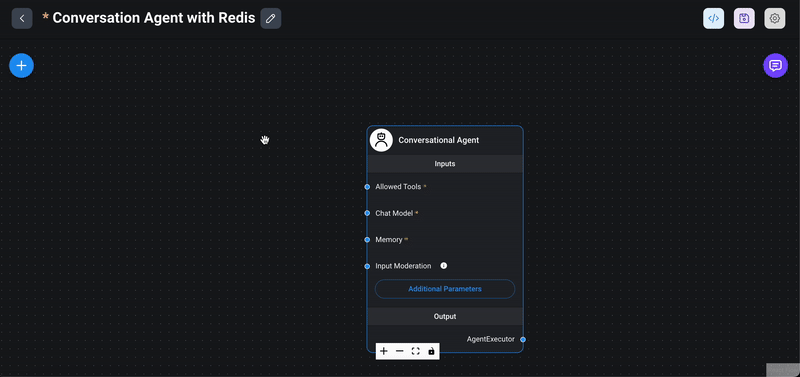
1> Drag the conversational agent node: From the `Agents` section in the Flowise interface, drag the `Conversational Agent` node into your chatflow workspace.
2> Modify additional parameters: In the node's interface, you have the option to modify the system message prompt. This prompt is used to set the context for the chatbot, ensuring it understands the specific domain or behavior you want it to exhibit. Also, click on the save icon to ensure your modifications are not lost.
By following these steps, you will have successfully added a conversational agent node to your chatflow and set the initial context for your chatbot. In subsequent sections, we will integrate additional nodes and configure the chatbot to interact with Redis and other specialized agents.
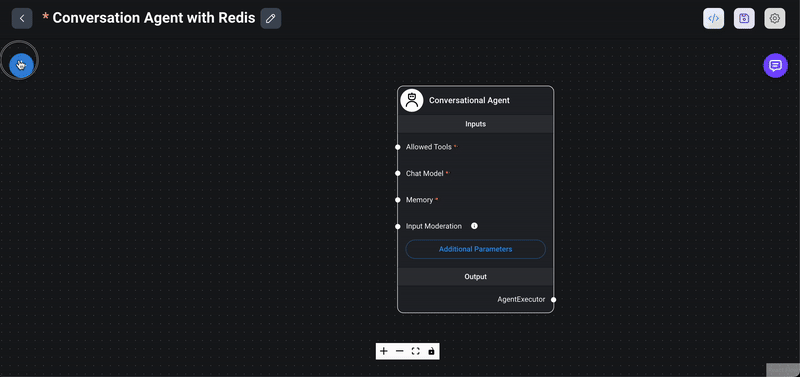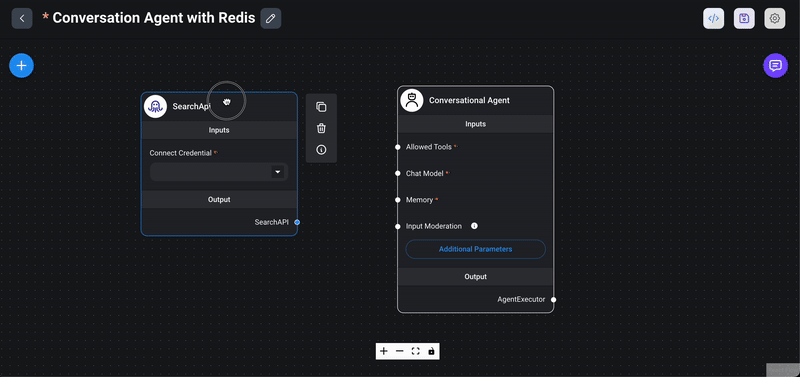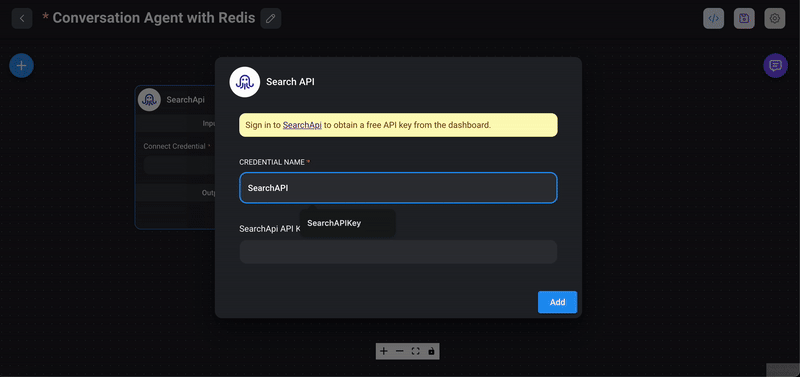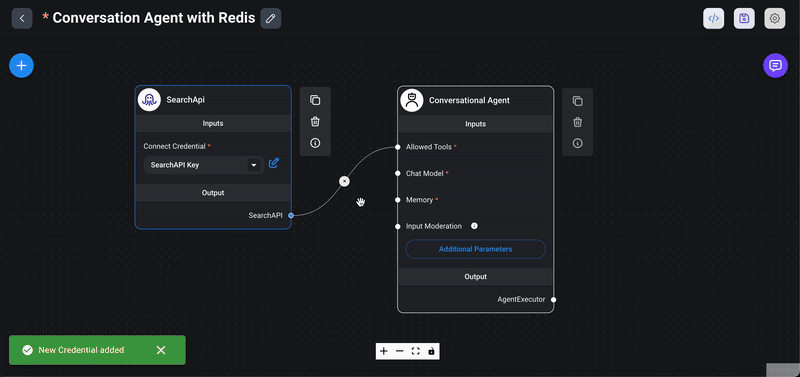
1> Drag the SearchAPI node: From the `Tools` section in the Flowise interface, drag the `SearchAPI` node into your chatflow workspace. The SearchAPI node acts as an agent capable of fetching data from Google search results.
2> Connect to conversational agent node: Connect the `SearchAPI` node to the `Conversational Agent` node by drawing a line from the output of the `Conversational Agent` node to the input of the `SearchAPI` node. This connection allows the conversational agent to utilize the search capabilities provided by the `SearchAPI`.
3> Set the SearchAPI key: In the interface of the SearchAPI node, enter your SearchAPI key. This key is necessary for the node to authenticate and perform search queries.
4> Combine multiple tools: You can enhance the capabilities of your Conversational Agent by adding multiple tools. For example, you can integrate `SearchAPI, Calculator, Python Interpreter or Custom Tool` node. The Conversational Agent will automatically select the appropriate tool to handle specific types of queries. For this demo, we will be just adding `SearchAPI` node. Also, click on the save icon to ensure all configurations and connections are stored.
By following these steps, you will have successfully integrated a SearchAPI node into your chatflow, let's add other nodes in next steps.
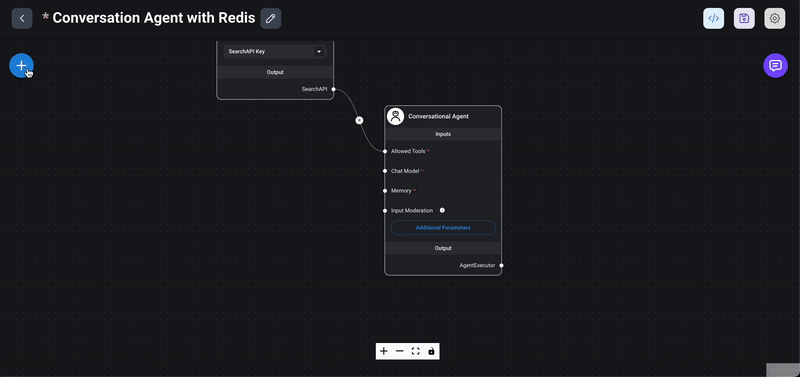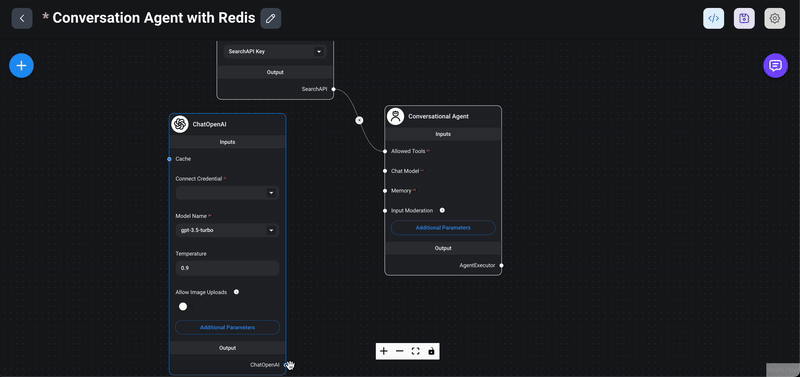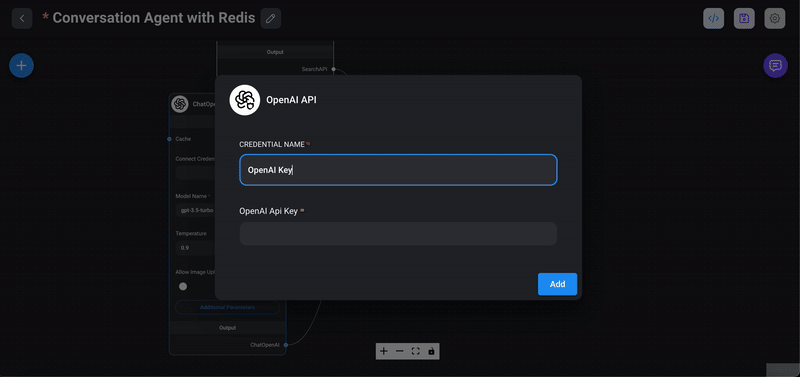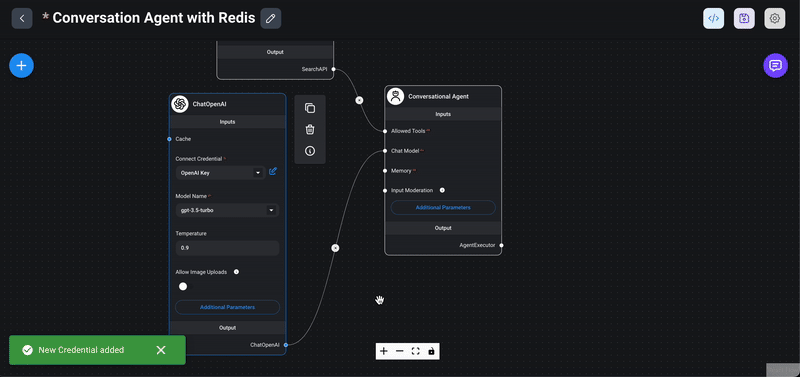
1> Drag the ChatOpenAI node: From the `Chat Models` section in the Flowise interface, drag the `ChatOpenAI` node into your chatflow workspace.
2> Create an OpenAI key: If you haven't already created an OpenAI key, do so by clicking on the `Create New` menu within the node's interface. This key is essential for authenticating requests to the OpenAI API.
3> Choose a model: Select a model like GPT-3, GPT-4 ..etc from the available options. The model determines the behavior and capabilities of your conversational agent.
4> Set the temperature: The temperature parameter controls the randomness of the model's responses. It ranges from 0 to 1:
- Low temperature (e.g., 0.2): Produces more deterministic and focused responses.
- High temperature (e.g., 0.8): Produces more creative and varied responses.
5> Set additional parameters: Configure other parameters such as `Max Tokens`, which defines the maximum number of tokens (words or parts of words) the model can generate in a single response. Ensure you save your chatflow regularly to preserve all changes.
By following these steps, you will have successfully added and configured a `ChatOpenAI` node in your chatflow. This node will serve as the core conversational engine, leveraging OpenAI's powerful language models to generate responses. In subsequent sections, we will further enhance your chatflow with additional nodes.
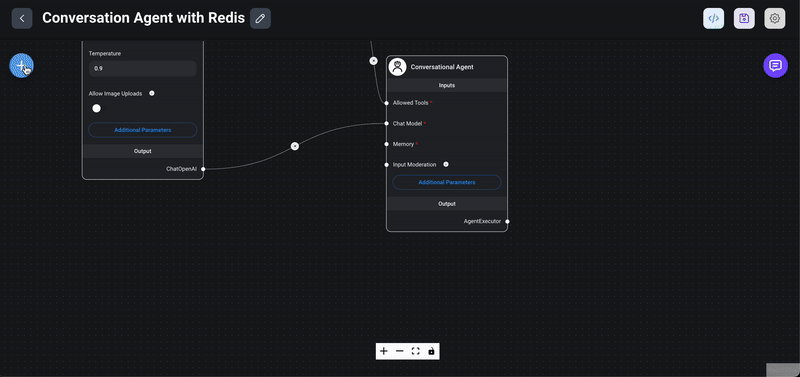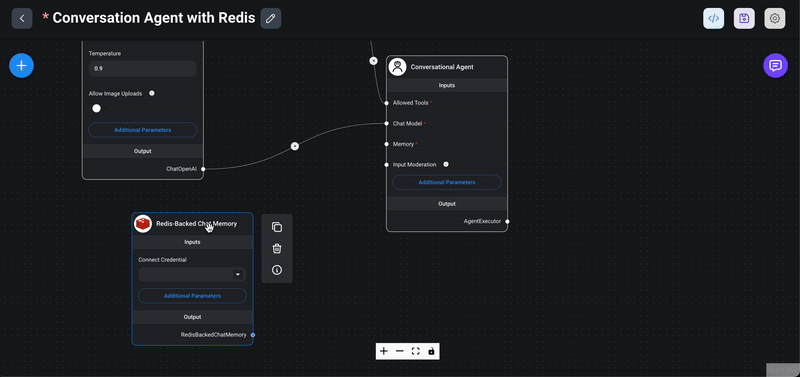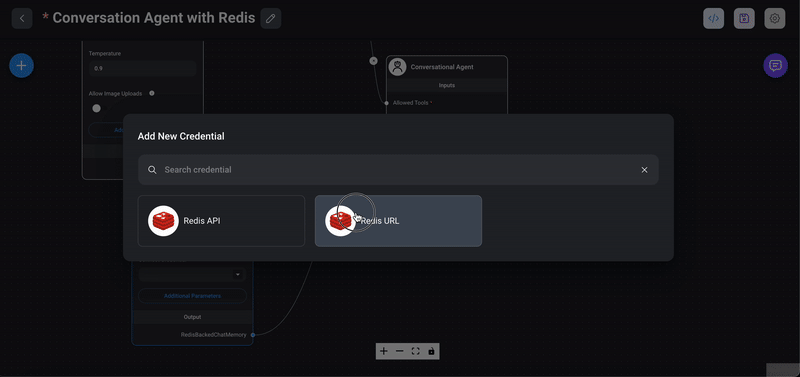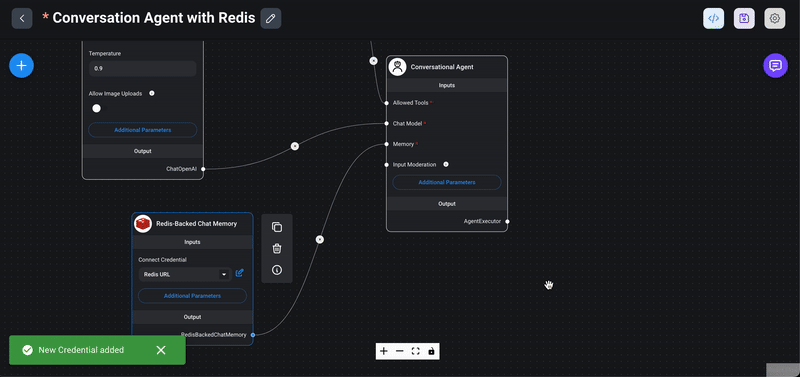
1> Drag the Redis chat memory node: From the `Memory` section in the Flowise interface, drag the `Redis Backed Chat Memory` node into your chatflow workspace.
2> Choose Redis connection key: In the node's interface, choose or create a connection key for the Redis instance. This connection key will be used to store and retrieve chat memory data.
3> Set chat key prefix: In the additional parameters section, you can set a chat key prefix. This prefix helps in organizing and identifying the chat memory records stored in Redis. Finally, save your chatflow to ensure all configurations and connections are persisted.
Why Use Redis for chat memory?
Speed: Redis is an in-memory data store, which means it can quickly read and write data, providing low-latency access to chat history. This speed is crucial for maintaining a seamless and responsive conversational experience.
Persistence: Redis also supports persistence, allowing chat data to be stored permanently. This means even if the application restarts or crashes, the chat history can be recovered, ensuring continuity in conversations.
By following these steps, you will have successfully added a Redis chat memory node to your chatflow. This integration ensures that your conversational agent can remember and utilize past interactions, enhancing the overall user experience. In the next section, we will test the chatflow setup.
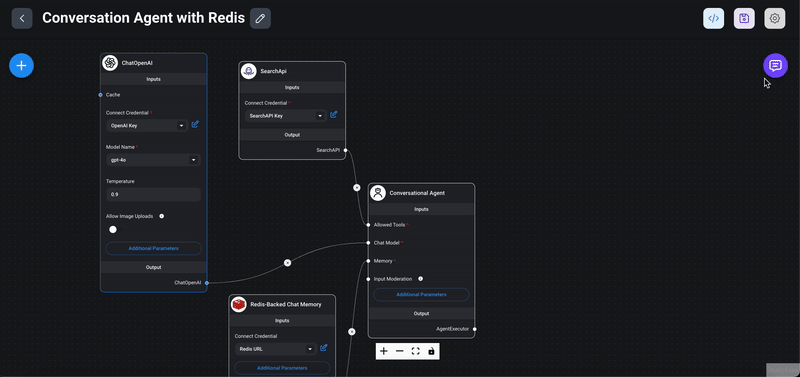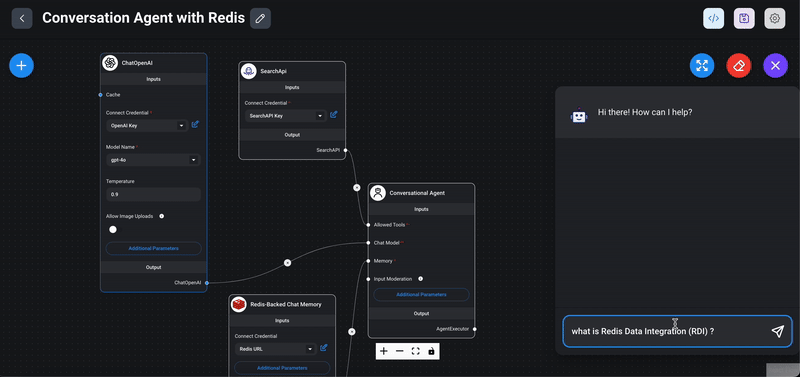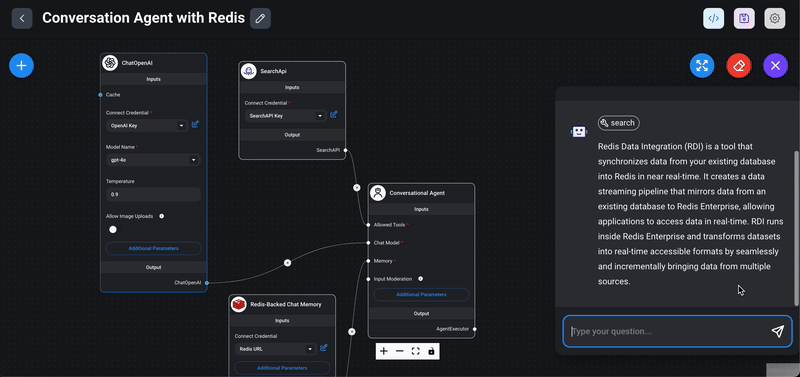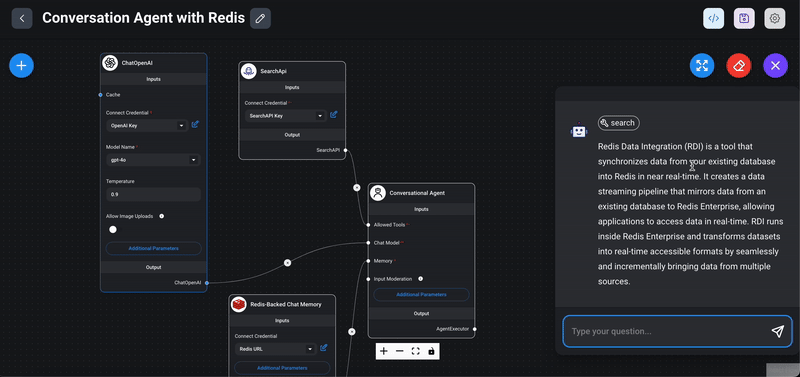
1> Start the chat: Click on the chat icon to interact with your newly created conversational agent.
2> Ask questions: Test the functionality by asking any questions on latest news/ events.
3> Check the response: Evaluate the response provided by the chatflow. Ensure that it correctly fetches and presents information based on the connected tools (e.g., SearchAPI). Click on the tool button above the chatflow response message to view details of the tools used.
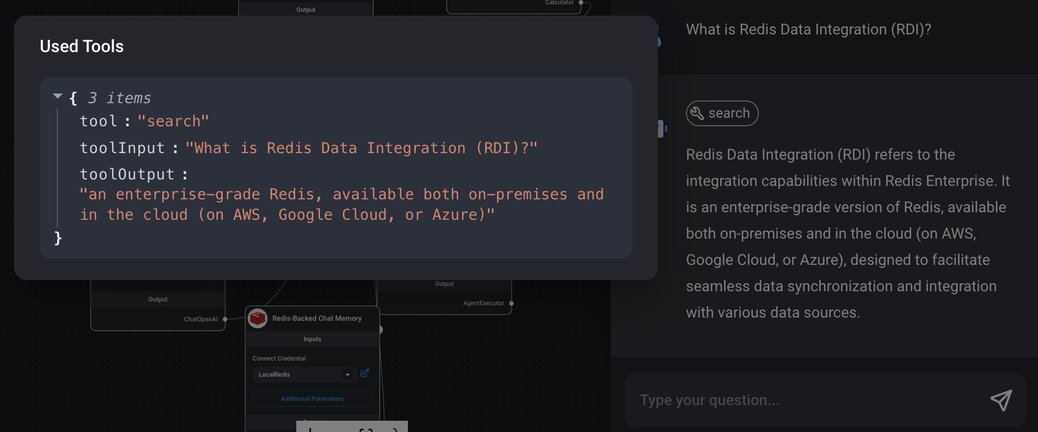
By following these steps, you will be able to test and validate the functionality of your chatflow, ensuring that your conversational agent is working as expected and providing accurate and relevant responses.
RedisInsight is a powerful GUI tool that allows you to interact with Redis data visually. It provides an easy way to verify and manage the persisted data in your Redis instance.
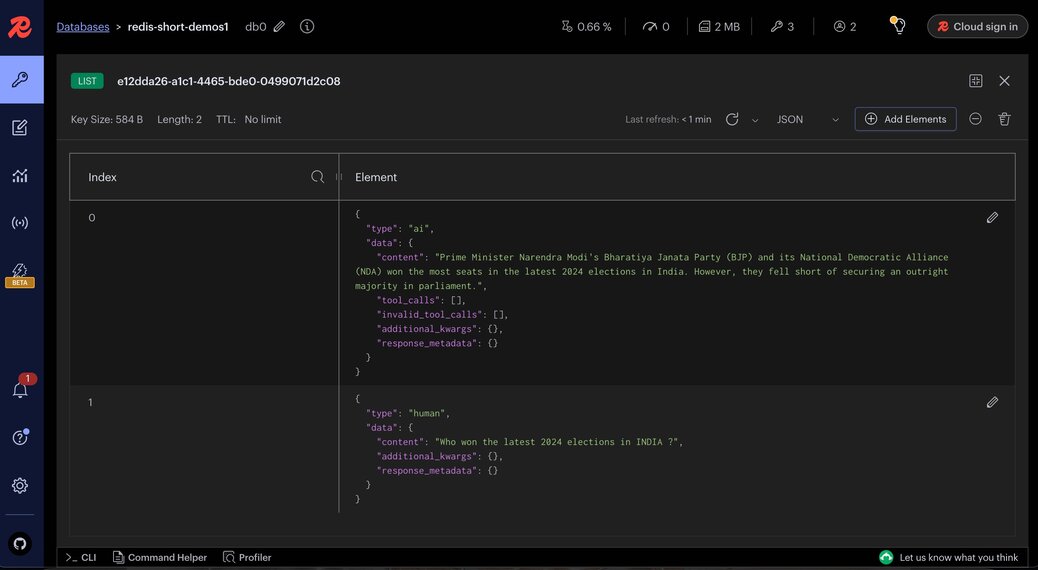
Example of stored chat data
In our example, Redis stores the chat data in a list with each entry representing a message in the conversation. Here are samples of how these entries might look:
[
{
"type": "ai",
"data": {
"content": "Prime Minister Narendra Modi's Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) and its National Democratic Alliance (NDA) won the most seats in the latest 2024 elections in India. However, they fell short of securing an outright majority in parliament.",
"tool_calls": [],
"invalid_tool_calls": [],
"additional_kwargs": {},
"response_metadata": {}
}
},
{
"type": "human",
"data": {
"content": "Who won the latest 2024 elections in India?",
"additional_kwargs": {},
"response_metadata": {}
}
}
]Type: Indicates the origin of the message. It can be either ai (response generated by the AI) or human (message input by the user).
Data:
- Content: The main text of the message. For AI responses, this is the generated answer. For human messages, this is the user's input.
- Tool calls: A list of calls made to external tools or APIs during the generation of the response.
- Invalid tool calls: A list of tool calls that failed or were invalid.
- Additional kwargs: Additional keyword arguments that might have been used during the message processing.
- Response metadata: Metadata associated with the response, such as timestamps or processing details.
By using RedisInsight, you can easily monitor and manage the data generated by your conversational agent, ensuring that all interactions are correctly logged and stored in Redis. This can be invaluable for debugging, improving the agent's performance, and maintaining a high-quality user experience.
Flowise allows you to easily export and import chatflows, enabling you to save your work for future use or share it with others. Below are the steps to export and import chatflows.
Exporting a chatflow
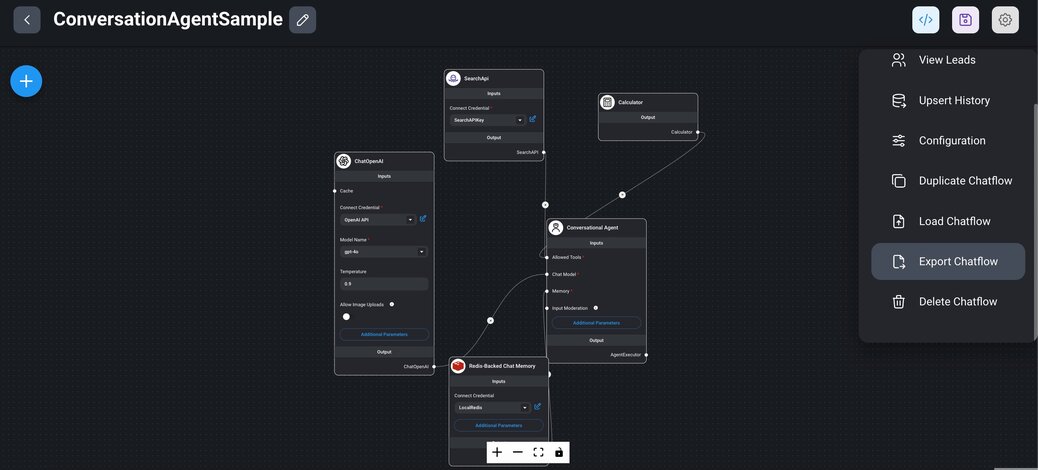
1> Select an existing chatflow: Go to the `Chatflows` menu in the Flowise interface. Choose the chatflow you want to export from the list of existing chatflows.
2> Export the chatflow: Click on the settings icon and select the `Export Chatflow` menu item. The chatflow will be exported as a JSON file, which you can download and save for future use.
Importing a chatflow
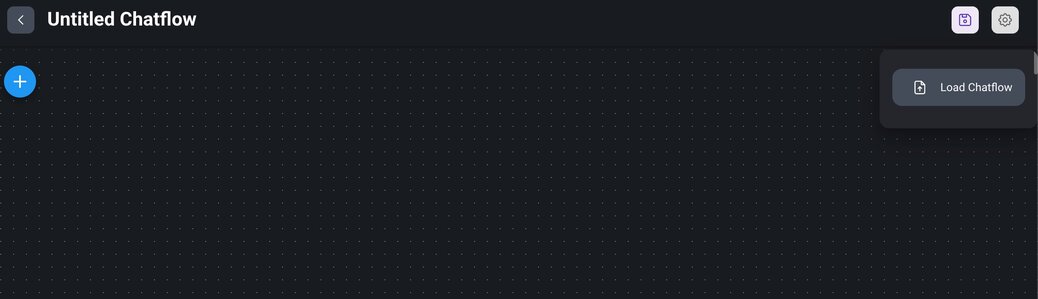
1> Create a new chatflow: Go to the `Chatflows` menu in the Flowise interface. Click on the `+ Add new` button to create a new chatflow.
2> Import the chatflow: Click on the settings icon and select the `Load chatflow` menu item. Upload the previously exported JSON file.
3> Configure the imported chatflow: The imported chatflow will appear without credentials. Ensure you provide the necessary credentials for any nodes requiring authentication (e.g., OpenAI key, SearchAPI key and Redis key) and save the chatflow to persist the changes. Once the chatflow is imported and configured, initiate a chat session to ensure it works as expected.
By following these steps, you can efficiently export and import chatflow in Flowise, facilitating easy backup, sharing, and reuse of your conversational agent.
By following this tutorial, you have successfully built a sophisticated conversational agent using Flowise and Redis. Flowise's intuitive interface and powerful integration capabilities, combined with Redis's speed and persistence, provide a robust platform for creating and deploying highly interactive and responsive AI chatbots. With these tools, you can handle complex queries, fetch real-time data, and maintain seamless user interactions.
In addition to using chat memory in Flowise, you can also leverage Redis as a vector store to store and retrieve embeddings for your conversational agent. This functionality is beneficial for tasks such as semantic search, recommendation systems, and more.
Below sample chatflow demonstrates how to use Redis as a vector store to perform semantic search using the RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) concept.
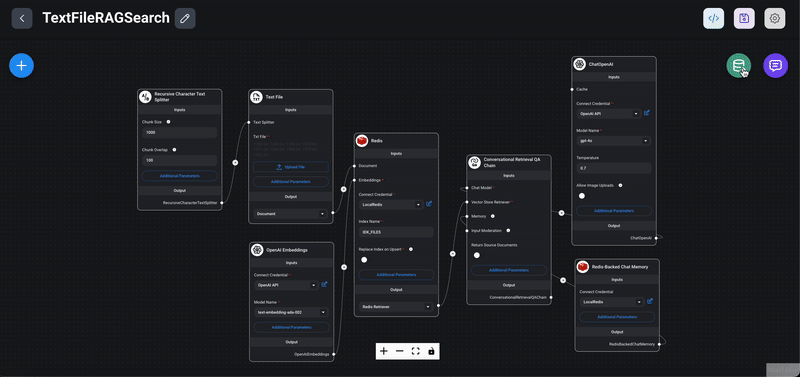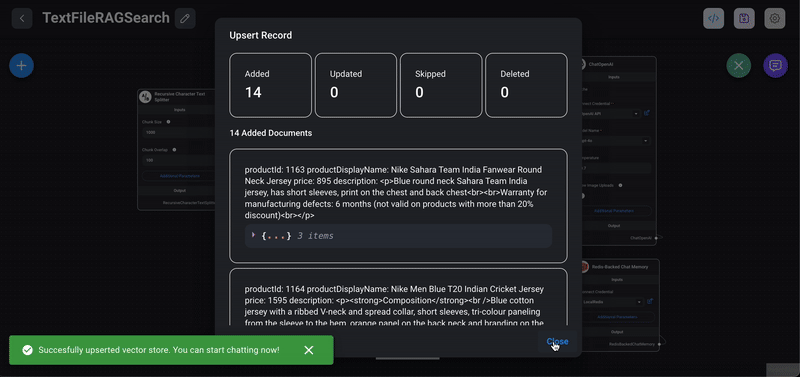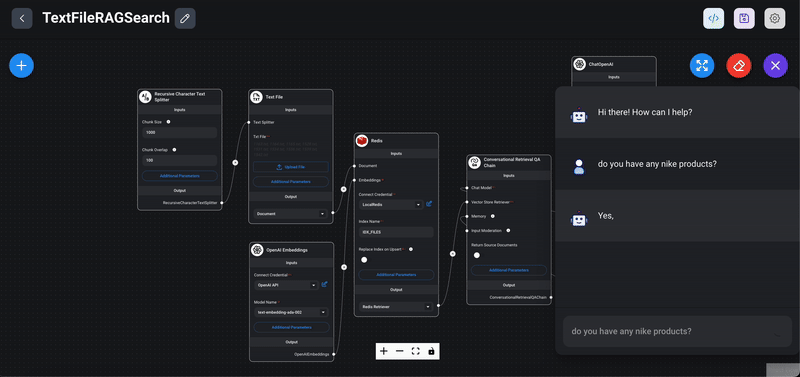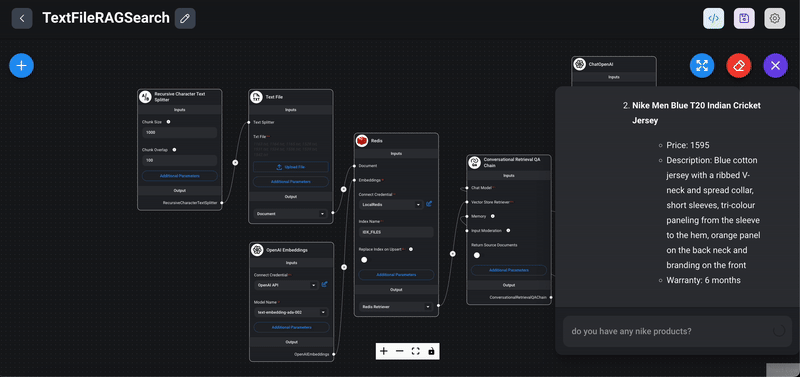
Quick steps to use the advanced example
1> Import the Chatflow: Download and import the provided chatflow JSON file into Flowise and save it.
2. Configure Nodes:
- Redis Node: Set up the Redis nodes with your connection key.
- OpenAI Node: Configure the OpenAI nodes with your API key and necessary parameters.
3> Upload Sample Data: Unzip and upload the provided sample products or any other text files into the `Text File` node of this chat flow. The uploaded data will be used for semantic search and recommendations.
4> Test the Chatflow: Initiate the chatflow and perform searches or queries to see how the system retrieves and utilizes the embeddings stored in Redis to generate meaningful responses.